The OptiX OSN 580 is a packet- and TDM-oriented new-generation multi-service optical transmission system, which is positioned at the convergence layer and access layer among Huawei's end-to-end Hybrid multi-service transmission platform (MSTP) product se
Consult
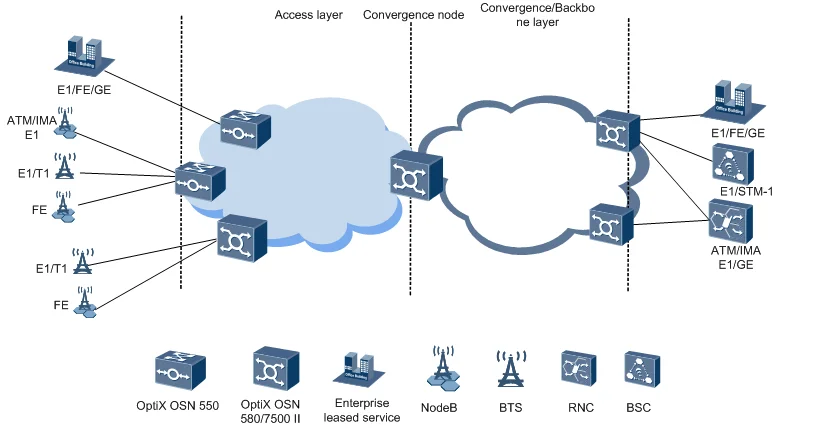
The OptiX OSN 580 is a device used at the access and convergence layers, which features large capacity, high availability, low power consumption, and compact structure. The OptiX OSN 580 supports:
The OptiX OSN 580 has a universal switch architecture, as shown in Figure 1. The OptiX OSN 580 supports coexistence of the time division multiplexing (TDM) domain and packet transport network (PTN) domain, which achieves smooth evolution from the TDM domain to the PTN domain while allowing the on-demand configuration and application of pure TDM services and packet services.
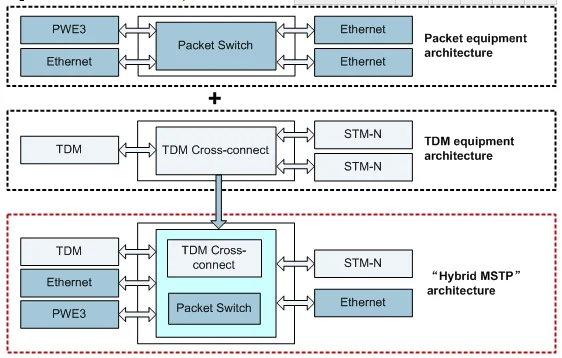
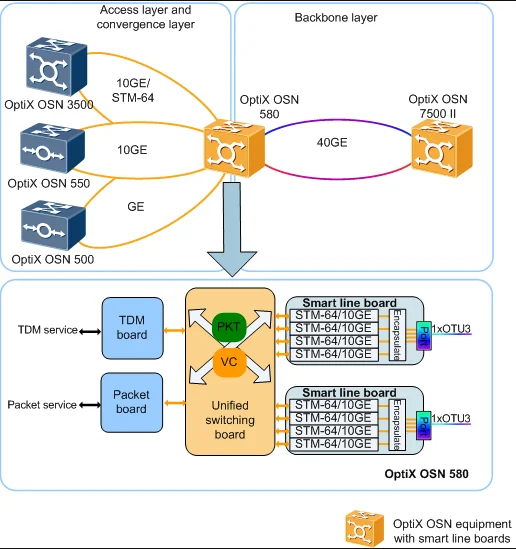
The OptiX OSN 580 supports the access and transmission of PDH, SDH, Ethernet, and MPLS-TP services.
In the PTN domain, the OptiX OSN 580 performs highly efficient statistical multiplexing of data services to reduce the service transport cost per bit. In the TDM domain, the OptiX OSN 580 incorporates SDH functions to ensure the high transport quality of Native TDM services (mainly voice services).
The OptiX OSN 580 supports switching of packet and VC granular services to address the requirement on transmitting SDH and packet services at the same time. The OptiX OSN 580 uses smart line boards so that:
Compared with legacy TDM networks, PTN networks have the following characteristics in terms of O&M:
To address those issues, the equipment uses the TP-Assist to provide more O&M means and simplify O&M operations for PTN networks during installation, commissioning, service configuration, fault locating, and routine maintenance. With the TP-Assist, PTN networks have the SDH-like O&M capabilities, which reduce the technical requirements for O&M personnel and improve O&M efficiency.
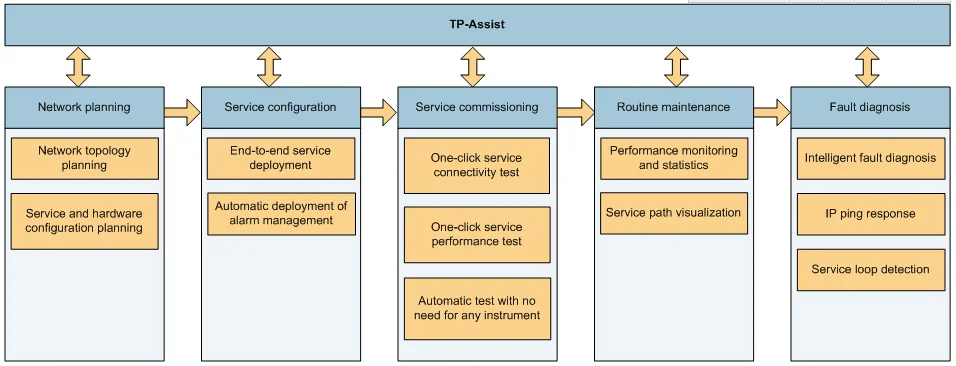
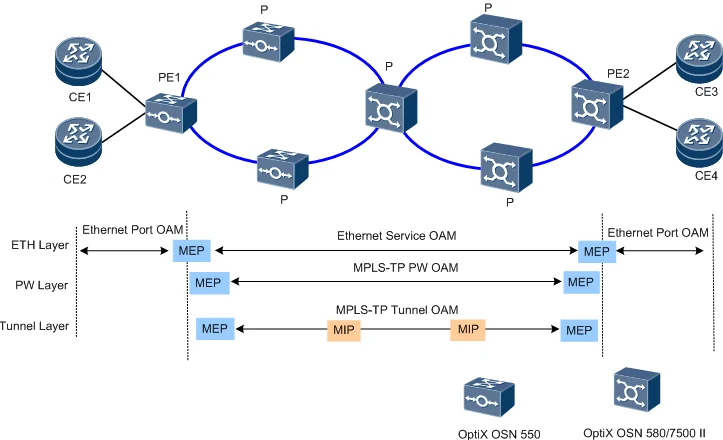
The OptiX OSN 580 supports the hierarchical OAM functions and have the SDH-like O&M capabilities. It can quickly detect and locate faults at each layer.
The hierarchical OAM functions include ETH OAM and MPLS-TP tunnel/PW OAM. Figure 4 shows the application of hierarchical OAM.
| Item | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance |
Chassis Dimensions (H x W x D): 221 mm x 442 mm x 224 mm
|
||
| Board |
For services and ports supported by the preceding boards, see Table 1. |
||
| Packet switching capacity | 280 Gbit/s | ||
| TDM access capacity | 280 Gbit/s | ||
| Equipment-level protection |
|
||
| Intelligent fan speed adjustment | Supports the automatic adjustment of fan speed based on the highest temperature of the board in the chassis. | ||
| Management ports and auxiliary ports | Interface Type | Description | Connector |
| External clock port | 120-ohm external clock port, which can work in 2048 kbit/s mode or 2048 kHz mode | RJ45 | |
| Power supply port | Power supply port connecting to two -48/-60 V DC power supplies | 2 mm HM connector | |
| Two 110 V/220 V AC power supply ports | Three-phase socket | ||
| Network management port | Ethernet NM port/NM cascading port, which is connected to a network management system (NMS) | RJ45 | |
| Alarm input/output port | 6-input/2-output alarm port | RJ45 | |
| Board Classification | Board Acronym | Board Name | Port Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| System control, switching, and timing board | TNW1UCX |
The cross-connect, timing, system control, and line board supports:
|
|
| Packet processing board | TNW1EM20 | 12xGE+8x10GE/GE switching and processing board |
|
| SDH boards | TNH2SL1Q | 4xSTM-1 optical/electrical interface board | STM-1 SFP optical/electrical port. The optical port type can be S-1.1, L-1.1, or L-1.2. STM-1 ports support SFP electrical modules. |
| TNH2SL4D | 2xSTM-4 optical interface board | STM-4 SFP optical port. The optical port type can be S-4.1, L-4.1, or L-4.2. | |
| TNW1SL41O | 8xSTM-4/STM-1 line board |
|
|
| TNW1SL16Q | 4xSTM-16 line board | STM-16 SFP optical port. The optical port type can be S-16.1, L-16.1, or L-16.2. | |
| TNW1SL64S | 1xSTM-64 line board | STM-64 SFP optical port. The optical port type can be I-64.1, S-64.2b, or P1L1-2D2. | |
| TNW1SL64D | 2xSTM-64 line board | STM-64 SFP optical port. The optical port type can be I-64.1, S-64.2b, or P1L1-2D2. | |
| PDH boards | TNH2SP3D | 42xE1/T1 tributary board | 42-channel 75/120-ohm E1 interface or 100-ohm T1 interface |
| TNH2PL3T | 3xE3/T3 tributary board | 3x75-ohm E3/T3 interface | |
| Smart line boards | TNW1HUND2 | Two-channel 10 Gbit/s line service processing board | Two-channel DWDM-compliant OTU2 optical signals |
| TNW1HUNS3 | 40 Gbit/s hybrid service processing board providing a single optical port | One-channel DWDM-compliant OTU3 optical signal | |
| WDM boards | TNM1DMD2 | Two-channel bidirectional optical add/drop multiplexing board |
|
| TNM1MR2 | Two-channel optical add/drop multiplexing board |
|
|
| Auxiliary boards | TNM1AUX | Auxiliary interface board |
|
| Power boards | TNF5PIU | Power board | One-channel -48/-60 V DC power input port |
| TNF5APIU | Power board | One-channel 110/220 V AC power input port | |
| Fan board | TNW1FAN | Fan board | Not involved |
Table 4-1 OptiX OSN 580 packet functions and features
| Item | Description | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPLS functions |
The packet switching unit of the UCX board works with a service board to implement MPLS-TP functions.
|
|||
| PWE3 functions |
The packet switching unit of the UCX board works with a service board to implement PWE3 functions.
|
|||
| Packet system performance | See Table 1. | |||
| Service | Service Category | Maximum Receiving Capability | Service Port | |
| Description | Connector | |||
|
Ethernet service:
|
FE (electrical port): 120 | 10/100BASE-T(X) | RJ45 | |
| FE (optical port): 120 |
|
LC | ||
| GE (optical port): 120 |
|
LC | ||
| GE (electrical port): 120 | 1000BASE-T | RJ45 | ||
| 10GE (optical ports): 48 |
|
LC | ||
| Protection | Tunnel APS |
Complies with the ITU-T G.8131 standard.
NOTE:
Tunnel APS and PW APS share 4k protection group resources. |
||
| PW APS |
Complies with the ITU-T G.8131 standard.
NOTE:
Tunnel APS and PW APS share 4k protection group resources. |
|||
| ERPS |
Supports ERPS that complies with ITU-T G.8032 and ITU-T Y.1344.
NOTE:
Only Native E-LAN services support ERPS. |
|||
| LPT |
Complies with the Huawei proprietary protocol.
|
|||
| LAG |
Complies with the IEEE 802.3ad and IEEE 802.1AX standards.
|
|||
| MC-LAG |
Complies with the IEEE 802.3ad and IEEE 802.1AX standards.
|
|||
| Maintenance | MPLS-TP OAM |
Complies with the ITU-T G.8113.1 standard.
NOTE:
The total number of tunnel OAM, PW OAM, and ETH OAM resources must not exceed 8k. |
||
| ETH OAM |
Complies with the IEEE 802.3ah and IEEE 802.1ag standards.
NOTE:
|
|||
| RMON |
Supports port-level and service-level RMON functions, in compliance with RFC 1757 and RFC 2819. Supports four RMON management groups: Ethernet statistics group, Ethernet history group, and Ethernet history control group. Port level:
Service level:
|
|||
| SNMP | Queries port information and port/service performance statistics using a standard SNMP terminal. | |||
| Port mirroring |
Supports port mirroring that enables Ethernet service analysis and service fault diagnosis without affecting the services.
|
|||
| Synchronization | Synchronous Ethernet clock |
NOTE:
SFP electrical modules do not support synchronous Ethernet clocks. |
||
| Others | HQoS |
|
||
Table 4-2 OptiX OSN 580 TDM functions and features
| Item | Description | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Service | Service Category | Maximum Receiving Capability | Service Port | ||
| Description | Connector | ||||
| SDH service |
|
|
|
||
| 112xSTM-4 | S-4.1, L-4.1 and L-4.2 optical ports | LC | |||
| 56xSTM-16 | S-16.1, L-16.1 and L-16.2 optical ports | LC | |||
| 28xSTM-64 | I-64.1, S-64.2b, I-64.1b, and P1L1-2D2 optical ports | LC | |||
| PDH service |
168xE1/T1 |
E1 (75/120-ohm)/T1 (100-ohm) electrical ports | Anea 96 | ||
| 12xE3/T3 | E3 (75-ohm)/T3 (75-ohm) electrical ports | SMB | |||
| TDM network protection | SNCP |
|
|||
| Ring MSP |
|
||||
| Linear MSP |
|
||||
| Maintenance | PRBS | Supported | |||
| Synchronization | Physical layer clocks |
|
|||